CSS: The style of web pages
HTML was great for academic documents, but not great for marketing materials and definitely not great for full applications. People wanted a way to style their documents, and that is how we got CSS.
Building on our earlier example, let’s create a folder with two documents:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Demo app</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello, world!</p>
</body>
</html>This is the same as above, but with an added <link> tag (which is just telling the browser the address it can request to find an associated CSS file; because the address doesn’t begin with a / it’s presumed to be relative to the HTML file). And:
p {
color: red;
}This is a CSS file! It says that all paragraph tags, p, should have a text color of red.
You can open that HTML file to see it with the style applied. And, like our HTML example, we can continue to experiment using CodeSandbox:
Selectors
CSS is all about selecting elements and modifying their properties. CSS files are structured as lists of these rules, which use a selector to specify element(s) the rule applies to and lists properties to apply to those matched elements.
/**
* This is a c-style comment.
*
* This paragraph says all paragraph tags should be red.
*/
p {
color: red;
}
/* This paragraph says all headings should be bold and blue. */
h1 {
color: blue;
font-weight: bold;
}There are three main types of selectors:
foo: this matches all elements of the tagfoo(for example,<foo />)#foo: this matches the element with the attributeid="foo". Every ID must be unique..foo: this matches all elements which include the attributeclass="foo". Unlike IDs, there can be many elements with the same class; there can also be multiple classes per element; for example, an element withclass="foo bar"will match both.fooand.bar.
There are also attribute selectors, which match elements based on the value of an attribute, for example [type="text"] matches all tags with the type attribute set to text.
Composing selectors
Selectors can also be combined:
- Commas allow either selector to match (e.g.
#foo, #barapplies to either#fooor#bar) - Selectors can be concatenated so ALL selectors must match (e.g.
p#foo.barmatches anyptags with the IDfooand the classbar) - Spaces match descendents (e.g.
.foo .barmatches any element with classbarthat is a descendent of an element with classfoo) - Combinators can be used to build more complicated relationships (e.g.
.foo > .barmatches any element with classbarthat is a direct descendent of an element with classfoo)
Specificity
If two different selectors apply to an element:
- the properties in the selector with the most IDs in it wins (
#foohas 1 ID but#foo #barhas two IDs); - if both selectors have the same number of IDs, the properties in the selector with the most classes wins;
- if both selectors have the same number of classes, the properties in the selector with the most tags wins;
- if both selectors have the same number of tags, the properties in the selector defined later in the file wins.
This is called specificity.
CSS rules can be thought of as applying from lowest specificity upwards. So, if a rule sets the text color to red, and no higher specificity rule overrides it (or there is no higher specificity rule), the text color will still be red. (This is where the cascading of Cascading Style Sheets comes from).
Pseudo-selectors
Selectors can also match states. These selectors are prefixed with a colon. For example, .foo:hover matches elements with class .foo when the mouse hovers over them:
Properties
As I said, CSS is all about selecting elements and modifying their properties. Properties are all of the form property-name colon property-value (which sometimes includes a unit). For example,
width: 200pxwidth: is the property200pxis the value (pxis the unit, meaning pixels)
Values can either be:
- Enums (e.g.
text-decoration: underline): which are property specific. - Measurements (e.g.
width: 200px): that take the form of pixels (px), inches (in), as a percent of the screen’s height (vh), or something else entirely . Zero is always unitless (because it’s always the same). - Paths to other files (e.g.
background-image: url(./file.png)): the value is a filepath relative to the CSS file, and whileurl()may look like a function, it is just telling CSS the type of the value. The path can either be quoted or unquoted (like bash parameters, the quotes are only important if there is a space). - Colors (e.g.
color: red): which either take the form of names (e.g.red) or as triplets of red, green, and blue values (RGB ). If you’re new to digital graphics, an online color picker is a good way to build intuition mapping colors to RGB (rgb(255, 0, 0)) or hex(adecimal) values (#FF0000). (Note: there are other ways to specify colors, but they are less common.)
With CSS properties, you can do everything from change the cursor to full 3d transforms. While I can’t cover everything CSS can do , some basics you might encounter are:
- Text color:
color: red; - Text size:
font-size: 12px; - Bold text:
font-weight: bold; - Background color:
background-color: red;
Layout
One particularly important set of properties are those that effect the size and position of your elements.
By default, divs are arranged in one column from the top of the page to the bottom and have the height of their contents. This is one of three default layout kinds:
block: the element takes up a whole row (e.g.<div>)inline: a selection of text, the element takes up no space beyond the inner content (e.g.<span>)inline-block: something that has a height and width, but doesn’t need a full row to itself (e.g.<img>)
You can override the layout kind via the display property. For example, normally divs don’t show up next to each other, but by changing their display to inline-block we can get the browser to lay them out next to each other.
Sizing: the box model
As for how these elements are sized, no CSS tutorial would be complete without a discussion of the box model. The box model is a framework for how much space each element takes.
Each element is modeled as four concentric rectangles (or boxes):
- Content: the innermost box that contains the children of the element
- Padding: white space that includes the background
- Border: a line around the padding
- Margin: space outside the border separating the element from adjacent elements.
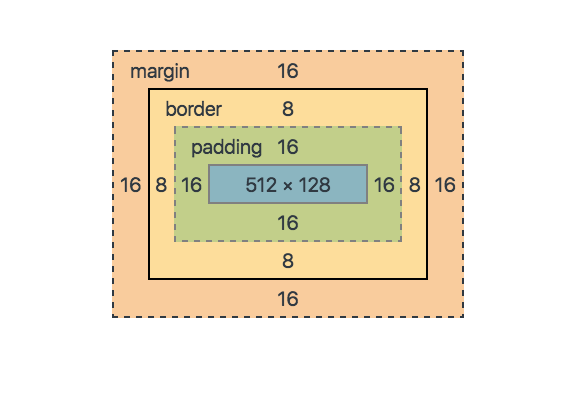
For each rectangle, you can define all sides at once (padding; 16px), each side individually (padding-left: 16px), or each side individually using a shorthand (padding: 16px 12px 8px 4px defines the top as 16px, right as 12px, bottom as 8px, and left as 4px).
The height and width of the content default to whatever height and width the children require to be laid out, but can be explicitly set via the height and width properties (e.g. height: 100px). In addition to specifying a height and width, you can also constrain them using max-height, max-width, min-width, and min-height. For example, an element with the example below will be as wide as possible, but not more than 800px:
.example {
width: 100%;
max-width: 800px;
}While height was intended to define height of the content, many developers assume it refers to height of the element (including the height of contents, padding, and border). For example, a developer that assigns a box a height of 16px and a padding of 4px, might be confused when the height of the element is 24px instead of 16px (4px top padding + 16px height + 4px bottom padding).
This confusion was sufficiently widespread (as was the desire to specify the overall height of the element) that css introduced the box-sizing property to allow developers to toggle whether height refers to the height of the content or the height of the element: box-sizing: border-box redefines height as content height + padding height + border height (the same applies to width).
So far, we haven’t talked much about margin, a word of caution there: many developers shy away from margin because doesn’t always behave intuitively. Specifically: if you have two div’s on top of each other with a margin of 10px, the total space between them will only be 10px (as both are at least 10px away from their neighbors). This is called margin collapsing .
Flex and Grid
While blocks and inline-blocks worked well for documents, they reached their limits with applications. For a long time people hacked <tables>’s for layout, then <div>’s became popular, but ultimately application UIs demanded something more. As a result, two layouts were introduced: flexbox and grid, which both let you define elements flexibly and in relation to other elements.
While the full APIs are probably more complicated than we have space to get into, there are wonderful tutorials:
- Flexbox: https://flexboxfroggy.com/
- Grid: https://cssgridgarden.com/
Positioning
Lastly, sometimes you want to position an element directly (rather than having the browser lay it out for you). In this case, you can position an element relative to:
- its parent: using
position: absolute - the browser window: using
position: fixed
Browser defaults
If you don’t define a property, the browser will fall back to its default; different tags have different defaults (for example, on Chrome, the <body> has a default padding of 8px). These defaults are not consistent across browsers. As a result, developers will frequently reset these properties themselves, and it is common to see declarations like the below in boilerplate projects:
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}To standardize CSS defaults across browsers, the idea of a “CSS Reset” was introduced:a stylesheet that overrides browser defaults. One of the more popular resets is normalize.css .
Devtools
You might be wondering, is that all it really is? Is every web page written this way? Yes, and I can prove it. If you’re using Chrome, right click on this page and click “Inspect” you’ll open up your browser’s developer tools panel (a similar concept exists in most browsers, but I’ll be focusing on Chrome’s).
The developer tools panel includes a variety of tools, but if you open “Elements” you’ll see the full HTML of the webpage, starting with the <html> tag (technically this is showing you the DOM, but more on that later). You can select an element to see its CSS and box model.
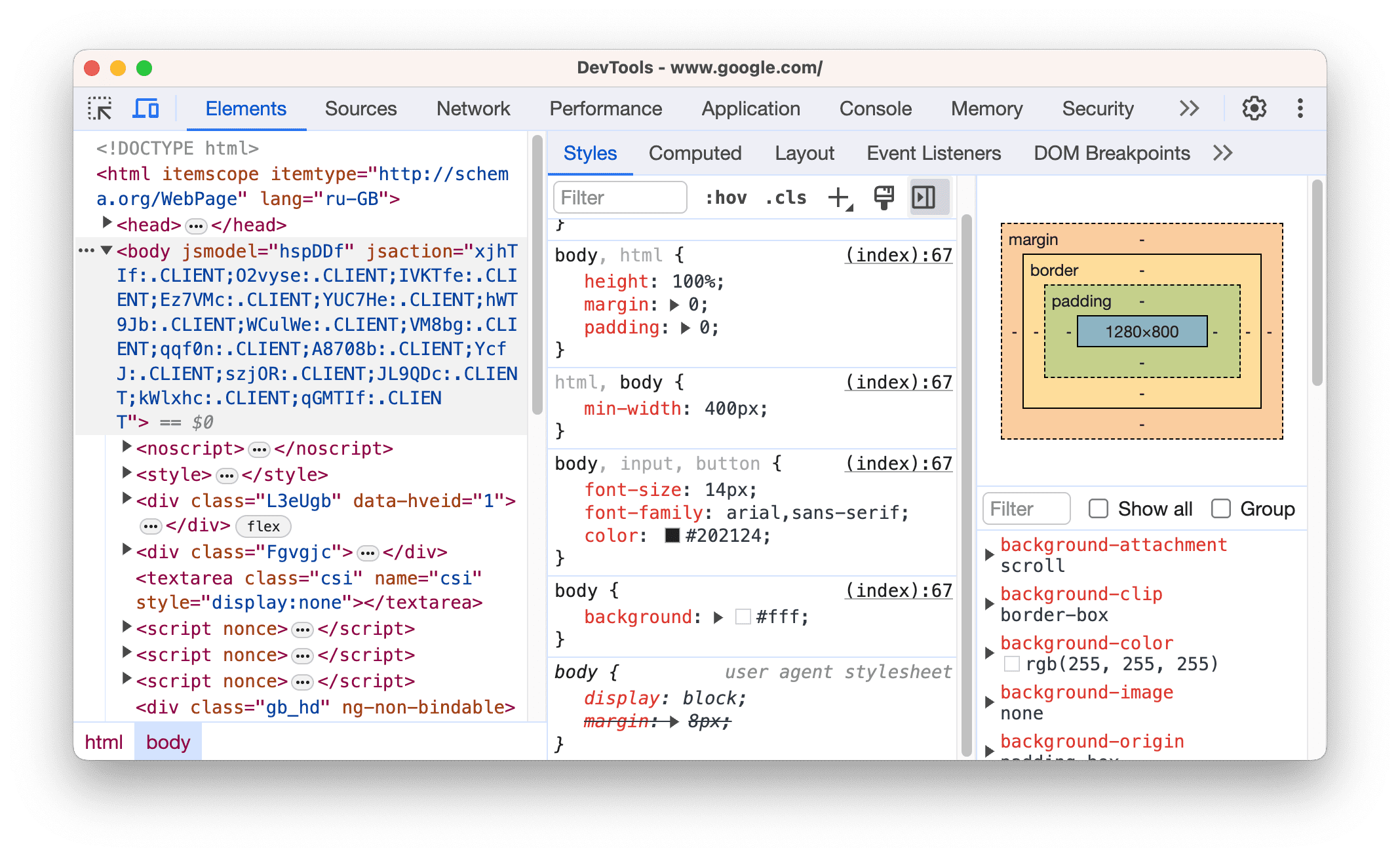
You can read more about the developer tools panel here ; the rest of the tools primarily help you debug any JavaScript running alongside the page, and we’ll get to that in the next chapter.
Advanced
There is no way to cover all of CSS in one chapter. There are simply too many properties. Even people who have been working with CSS for years still discover new properties (partially because new properties are also introduced regularly).
Hopefully, I’ve given you enough of a foundation to understand any new properties you run into. To that end, there are a few remaining concepts that could benefit from additional explanation. Here is a whirlwind tour.
Media queries
Media queries allow you to apply different CSS properties based on properties of the medium (most commonly, browser width or color scheme). This lets you have different designs for, for example, mobile vs desktop or light mode vs dark mode.
Variables
CSS has gotten more advanced over the years, and you can now specify properties that compose into other properties.
You can also compute things with calc (e.g. width: calc(80% - 10px). calc certainly has its place, but in general, I see first-time CSS developers overuse it. Calc is rarely necessary and leads to hard-to-understand code—that can be less performant—compared to using the browser’s native layout technologies (flex or grid).
Animations
There are two types of animations you can define in CSS. Transitions, which define how to change between different values of a property:
Animations, which animate an object:
Animations rely on “keyframes” : a concept borrowed from animation, you specify the properties at specific points, and let the runtime interpolate the middle state (for example, if you know that a box starts at 10px wide and ends at 20px wide, you can infer that half way through that animation, the box should be 15px wide).
Pseudo-elements
Selectors can also create elements. For example, .foo::before will create an element within all elements with class foo but before their children.
Yes this is weird; an example of when you might use it is to add a bullet point before items in a bullet point list.
